基础
-
类变量被声明为public static final类型时,类变量名称一般建议使用大写字母。
-
访问控制修饰符
当前类 同一包 子孙类(同一包) 子孙类(不同包) 其他包 public Y Y Y Y Y protected Y Y Y Y default Y Y Y private Y -
接口与抽象类 接口和抽象类都是继承树的上层,他们的共同点如下:
- 都是上层的抽象层。
- 都不能被实例化
- 都能包含抽象的方法,这些抽象的方法用于描述类具备的功能,但是不比提供具体的实现。
他们的区别如下:
- 在抽象类中可以写非抽象的方法,从而避免在子类中重复书写他们,这样可以提高代码的复用性,这是抽象类的优势;接口中只能有抽象的方法。
- 一个类只能继承一个直接父类,这个父类可以是具体的类也可是抽象类;但是一个类可以实现多个接口。
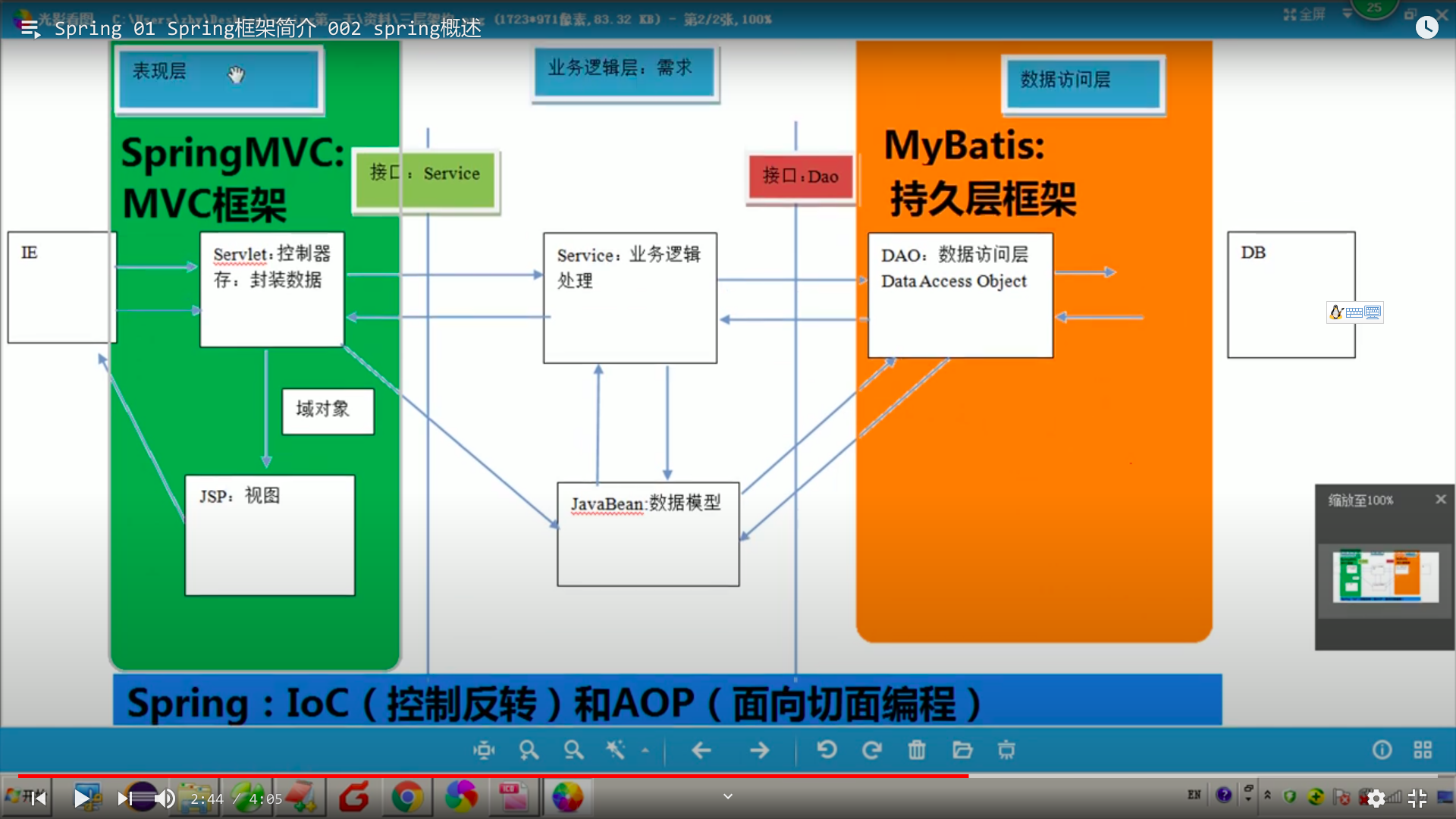
Spring
一、概述
- Inverse of Control
- Aspect Oriented Progamming
二、IoC
控制反转(Inversion of Control,缩写为IoC),是面向对象编程中的一种设计原则,可以用来减低计算机代码之间的耦合度。其中最常见的方式叫做依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI),还有一种方式叫“依赖查找”(Dependency Lookup)。通过控制反转,对象在被创建的时候,由一个调控系统内所有对象的外界实体,将其所依赖的对象的引用传递(注入)给它。
2.1 Bean的属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| class | packageName + className |
| id/name | 唯一标识 |
| scope | 作用域 |
| constructor-arg | |
| properties | |
| autowiring mode | |
| lazy-initialization | 延迟创建(启动时创建) |
| initialization | bean的所有必须属性被容器设置后调用的回调方法 |
| destruction | bean被销毁时调用的回调方法 |
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<!-- A simple bean definition -->
<bean id="" class="" >
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- A bean definition with lazy init set on -->
<bean id="" class="" lazy-init="true">
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- A bean definition with initialization method -->
<bean id="" class="" init-method="..." >
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- A bean definition with destruction method -->
<bean id="" class="" destroy-method="..." >
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions go here -->
</beans>2.2 Bean的作用域
| 作用域 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| singleton | 单例, 默认值 |
| prototype | 每次调用都产生新的实例 |
| request | 每次Http请求都会创建一个Bean, 仅作用于WebApplicationContext环境 |
| session | 同一个Http Session共用一个Bean, 仅作用于WebApplicationContext环境 |
| global-session | 一般用于Portlet应用环境,该运用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境 |
2.3 生命周期
<bean
id="hello"
class="com.example.Hello"
init-method="init"
destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="msg" value="这个msg属性的value"/>
</bean>Bean的销毁需要使用AbstractApplicationContext.registerShutdownHook()
2.4 Bean的继承
基于继承使用Bean模板
<bean id="beanTeamplate" abstract="true">
<property name="message1" value="Hello World!"/>
<property name="message2" value="Hello Second World!"/>
<property name="message3" value="Namaste India!"/>
</bean>
<bean id="helloIndia" class="com.tutorialspoint.HelloIndia" parent="beanTeamplate">
<property name="message1" value="Hello India!"/>
<property name="message3" value="Namaste India!"/>
</bean>三、依赖注入
3.1 基于构造函数的依赖注入
<beans>
<bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="2001"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="Zara"/>
</bean>
</beans>3.2 基于设值函数的依赖注入
<bean id="john-classic" class="com.example.Person">
<property name="name" value="John Doe"/>
<property name="spouse" ref="jane"/>
</bean>3.3 @Autowired
SpringBoot
一、AOP
-
@Aspect:声明该类为一个注解类;
-
@Pointcut:定义一个切点,后面跟随一个表达式,表达式可以定义为切某个注解,也可以切某个 package 下的方法
-
@Before: 在切点之前,织入相关代码;
-
@After: 在切点之后,织入相关代码;
-
@AfterReturning: 在切点返回内容后,织入相关代码,一般用于对返回值做些加工处理的场景;
-
@AfterThrowing: 用来处理当织入的代码抛出异常后的逻辑处理;
-
@Around: 环绕,可以在切入点前后织入代码,并且可以自由的控制何时执行切点;